How Do Illuminated Button Switches Improve User Awareness?
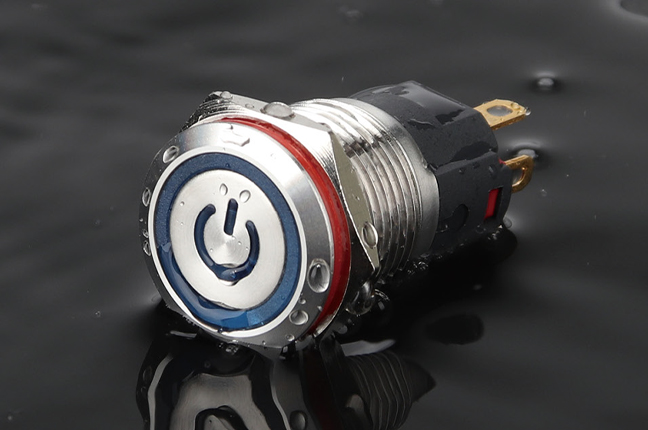
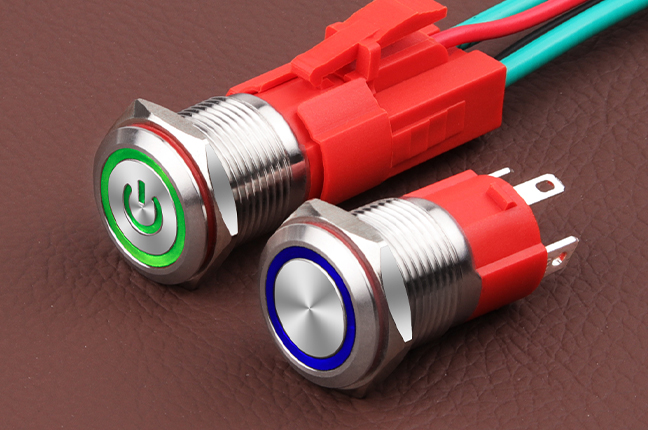
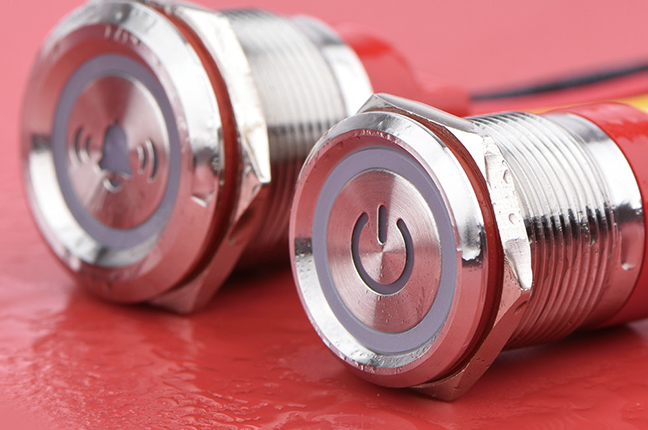
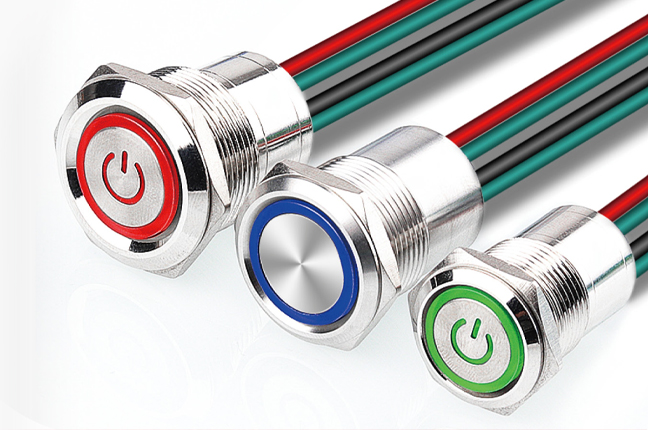
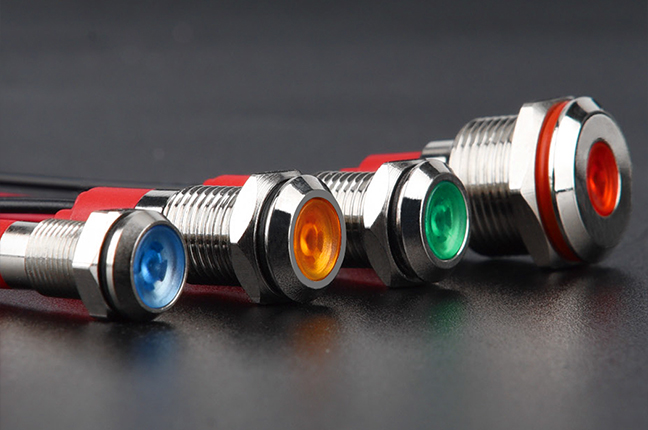
An Illuminated Button Switch combines a mechanical switching function with an integrated light source, usually LED-based. Its primary purpose is to provide visual feedback rather than simply triggering an electrical signal. The illumination can indicate system status, operational readiness, fault conditions, or mode selection.
From a practical standpoint, illuminated buttons are especially useful in environments where multiple control points exist or where ambient lighting is inconsistent. For example, in industrial cabinets, a lit pushbutton can show whether a circuit is energized or whether a machine is in standby. This reduces reliance on separate indicator lamps and simplifies panel layouts.
Color selection is not decorative; it often follows standardized conventions. Green may signal normal operation, amber can indicate standby or caution, and red is typically associated with abnormal states. Engineers must also consider voltage compatibility, as illumination circuits may differ from the control circuit itself. Proper wiring ensures that the light reflects the intended system condition rather than merely turning on when pressed.
Why Is a Stop Button Switch Critical for Safety?
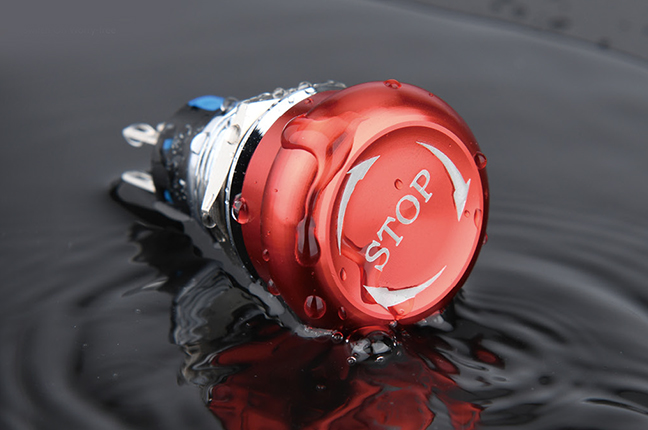
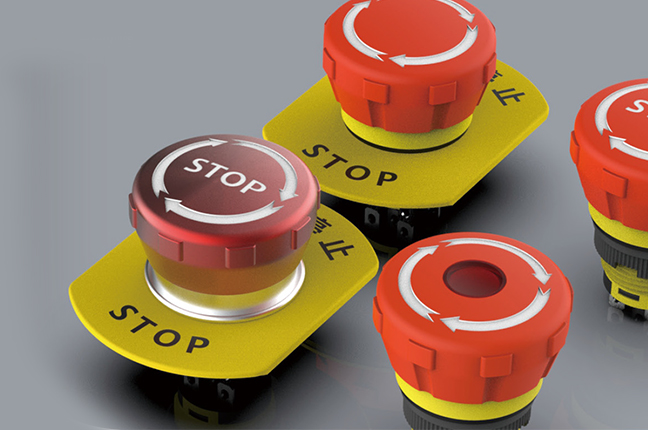
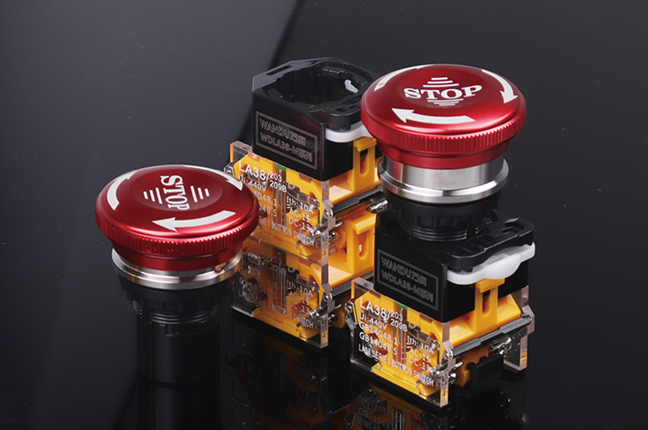
A Stop Button Switch serves a fundamentally different purpose: interrupting operation. Unlike start or mode-selection buttons, stop switches are designed with safety and immediacy in mind. Their function is not optional convenience but risk mitigation.
In industrial applications, stop buttons are positioned for quick access and are often configured as normally closed contacts. This design ensures that if a wire breaks or a terminal loosens, the circuit defaults to a stopped state rather than continuing operation unnoticed. Such logic is essential in compliance with many machinery safety standards.
The physical characteristics also reflect their role. Stop buttons usually have a larger actuator surface, higher actuation force, or distinct color contrast to reduce hesitation during use. In some cases, they are paired with emergency stop systems, though standard stop buttons should not be confused with emergency stop devices, which have stricter regulatory requirements. Understanding this distinction helps users avoid misapplication in safety-critical systems.
What Makes Metal Pushbutton Switches Suitable for Harsh Environments?
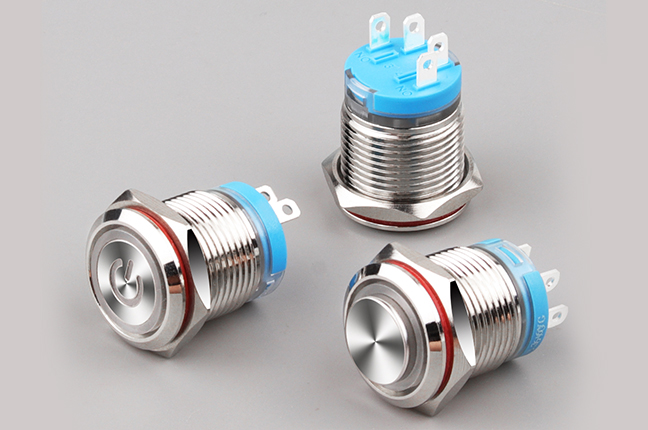
Metal Pushbutton Switches are selected primarily for their structural properties rather than a single electrical function. Their housings are commonly made from stainless steel, aluminum alloy, or brass, providing mechanical strength and resistance to external stress.
In environments exposed to vibration, dust, moisture, or frequent mechanical impact, metal-bodied switches maintain dimensional stability better than plastic alternatives. This stability helps preserve contact alignment over time, reducing issues such as intermittent signals or uneven actuation.
Another practical advantage lies in surface treatment. Many metal pushbuttons feature anodized, brushed, or polished finishes that improve corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning. This is particularly relevant in food processing equipment, outdoor installations, or transportation systems where hygiene and durability are ongoing concerns. However, metal housings also require attention to grounding and insulation design to ensure electrical safety.
How Should Users Choose Between These Switch Types?
Selection should begin with function rather than appearance. If system status needs to be clearly visible at a glance, an illuminated option adds measurable value. When operational interruption is the priority, a dedicated stop button with appropriate contact configuration is essential. In demanding physical conditions, metal construction addresses longevity and environmental exposure.
It is also common for these characteristics to overlap. A metal pushbutton may include illumination, or a stop button may be built into a metal housing. Evaluating specifications such as ingress protection rating, electrical life, mechanical life, and mounting depth provides a clearer picture than focusing on a single feature.
Key Takeaways for Practical System Design
These switch types reflect different layers of control logic: communication, protection, and durability. Illuminated buttons communicate system state, stop buttons enforce operational limits, and metal pushbuttons support reliable use under physical stress. Thoughtful integration of these elements reduces operator error, simplifies maintenance, and supports safer machine interaction. When applied with a clear understanding of their roles, these switches become functional tools rather than interchangeable panel components.


 русский
русский Español
Español